Have you learnt why deductions are extra beneficial than tax credit? Right here’s a rundown of fundamental tax points to know

Evaluations and proposals are unbiased and merchandise are independently chosen. Postmedia could earn an affiliate fee from purchases made by way of hyperlinks on this web page.
Article content material
When you don’t put together your individual tax return every year, you’re lacking out on what’s presumably the perfect schooling you may get about our Canadian tax system. Every week throughout tax season, I get dozens of emails from readers asking a wide range of questions. Many are wonderful and require a little bit of analysis for me to correctly reply. Others, nonetheless, present that some Canadians don’t actually have understanding of how our tax system works.
Commercial 2
Article content material
Article content material
Article content material
In truth, although, they’ll’t be blamed. Our private tax system, with its myriad deductions, credit, calculations, claw-backs, limitations and countless complexities just isn’t for the faint of coronary heart. However it’s necessary to have a fundamental understanding of why deductions are usually extra beneficial than tax credit, or why selecting to defer claiming a registered retirement saving plan (RRSP) contribution to a later 12 months could make sense.
This week, let’s return to fundamentals and take a more in-depth take a look at how the Canadian private tax system, with its progressive tax brackets, deductions and credit, works.
Let’s start with our tax brackets. People pay taxes at graduated charges, that means that your price of tax will get progressively increased as your taxable earnings will increase. The 2025 federal brackets are: zero to $57,375 of earnings (15 per cent); above $57,375 to $114,750 (20.5 per cent); above $114,750 to $177,882 (26 per cent); above $177,882 to $253,414 (29 per cent), with something above that taxed at 33 per cent. Every province additionally has its personal set of provincial tax brackets and charges.
Article content material
Commercial 3
Article content material
Whereas graduated tax charges are utilized to taxable earnings, not all earnings is included and sure quantities could also be deducted, thereby lowering the bottom to which marginal tax charges are utilized. For instance, capital positive factors are solely partially taxed. In contrast to peculiar earnings, comparable to employment earnings or curiosity earnings that’s absolutely included in taxable earnings, solely 50 per cent of capital positive factors are included in earnings, so the tax price is decrease than for peculiar earnings.
For instance, let’s say you realized capital positive factors of $10,000 from the sale of publicly-traded shares in 2024, and had no different capital positive factors or losses final 12 months. Solely 50 per cent of this quantity, or $5,000, could be taxed. If as a substitute you earned curiosity or web rental earnings of $10,000, you’d pay tax on all the quantity.
Frequent deductions that you could be subtract out of your complete earnings, thereby reducing your taxable earnings, embrace: RRSP and first house financial savings account (FHSA) contributions, transferring bills, childcare bills, curiosity expense paid for the aim of incomes earnings, funding counselling charges for non-registered accounts, and plenty of extra.
Commercial 4
Article content material
When you calculate the tax payable in your taxable earnings on the progressive charges above, you then calculate and deduct the varied non-refundable tax credit to which you will be entitled. In distinction to deductions, tax credit instantly scale back the tax you pay after marginal tax charges have been utilized to your taxable earnings. With tax credit, a set price is utilized to eligible quantities and the resultant credit score quantity offsets taxes payable.
Frequent non-refundable credit embrace: the fundamental private quantity, the spousal quantity, the age quantity, medical bills, tuition paid and charitable donations, amongst quite a few others. Almost all non-refundable credit are multiplied by the federal non-refundable credit score price of 15 per cent, which corresponds to the bottom federal tax bracket. Corresponding provincial or territorial non-refundable credit might also be out there, however the quantities and charges fluctuate by province or territory.
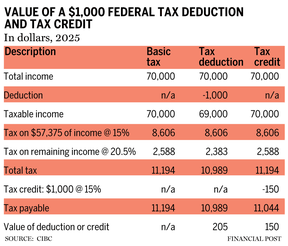
With this background, let’s take a look at an instance that reveals how a tax deduction yields tax financial savings on the marginal tax price that varies together with your earnings stage, whereas a tax credit score yields tax financial savings at a set price. Suppose you have got a complete earnings of $70,000 and declare both a $1,000 deduction (for, say, an RRSP contribution) or declare a federal non-refundable credit score for $1,000 (for, say, eligible medical bills past the minimal threshold).
Commercial 5
Article content material
The quantity of the deduction is subtracted from earnings, in order that this quantity of earnings just isn’t taxed. In column three within the accompanying chart, a $1,000 tax deduction yields $205 of federal tax financial savings, calculated because the $1,000 deduction multiplied by the marginal tax price that may have utilized to the earnings (20.5 per cent). Consequently, a deduction yields federal tax financial savings at your marginal tax price.
However, the $1,000 of eligible medical bills generates a federal non-refundable credit score of 15 per cent, yielding a federal tax financial savings of solely $150. While you add provincial or territorial tax financial savings to the federal financial savings above, the whole tax financial savings can vary from about 20 per cent for the mixed credit to greater than 50 per cent for a deduction, relying in your province or territory of residence.
Really useful from Editorial
The accompanying chart illustrates that until you’re within the lowest 15 per cent federal tax bracket (earnings under $57,535), tax deductions are typically extra beneficial than tax credit. There are some exceptions, comparable to for donations above $200 yearly, political contributions, and the eligible educator faculty provide tax credit score, the place the federal credit are price greater than 15 per cent.
Commercial 6
Article content material
Lastly, because the chart reveals, since a tax deduction saves tax at your marginal price, suspending a deduction (the place permissible, comparable to an RRSP or FHSA contribution) to a later 12 months while you’ll be in the next marginal tax bracket, implies that it could be price extra as its worth could be based mostly in your increased marginal price in that future 12 months.
Jamie Golombek, FCPA, FCA, CFP, CLU, TEP, is the managing director, Tax & Property Planning with CIBC Personal Wealth in Toronto. Jamie.Golombek@cibc.com.
When you favored this story, join extra within the FP Investor publication.
Bookmark our web site and help our journalism: Don’t miss the enterprise information you have to know — add financialpost.com to your bookmarks and join our newsletters right here.
Article content material

