The Pelvis will not be a hard and fast entity. There are joints which permit for the pelvis to change its form. In doing so, this enables for extra space for child throughout labor in addition to serving to the pelvic flooring to elongate in an effort to yield and assist the child throughout delivery.
Navigation
Understanding Pelvic Motion
The pelvis is split into 3 ranges: the inlet, mid-pelvis and the outlet. Every stage has the flexibility to widen and shut primarily based on the place of the legs and motion of the pelvis. For instance, when the legs are externally rotated, that means, the legs and toes are turned out like a ballerina, the highest of the pelvis, inlet, widens backward and forward. When the legs are turned in, the underside of the pelvis, the outlet, is wider backward and forward.
What does it imply to “open the pelvis”?
Whereas most yoga practitioners consider “hip opening poses” as simply huge exterior rotation positions, there are literally 6 actions of the hips. It’s necessary to make the most of all 6 actions to keep up a wholesome, balanced pelvis. In relation to methods to open the pelvis, we’re going to concentrate on 4 of those actions and the way every place impacts the form and area of the pelvis in a different way.

Exterior rotation: Legs are turned out. Opens the pelvic inlet backward and forward

Inside rotation: Legs are turned in. Opens the outlet backward and forward

Flexion: The leg is shifting in the direction of the torso. When the legs are above 90 levels, the sacrum strikes into nutation and the pelvic outlet widens from entrance to again.

Extension: The leg strikes away from the entrance airplane of the torso. This motion opens the pelvic inlet from entrance to again.
Sacral Motion and Pelvic Opening
We even have the place of the pelvis to contemplate! Let’s get a bit geeky and dive into among the nuances of the pelvis and its actions.
The pelvis is made up of three foremost components:
- Left and Proper Innominate Bones (Hip Bones): These meet within the entrance on the pubis symphysis, a joint product of cartilage.
- Sacrum: The triangular bone on the base of the backbone. It connects to the hip bones on the sacroiliac joints (SI joints).
- Coccyx (Tailbone): Situated on the very finish of the backbone.
The SI joints permit the sacrum and tailbone to maneuver independently of the hip bones. This motion is crucial for opening the totally different ranges of the pelvis throughout labor. Consider the sacrum like a entice door that may open to create additional area for the child.
Nutation and Counternutation
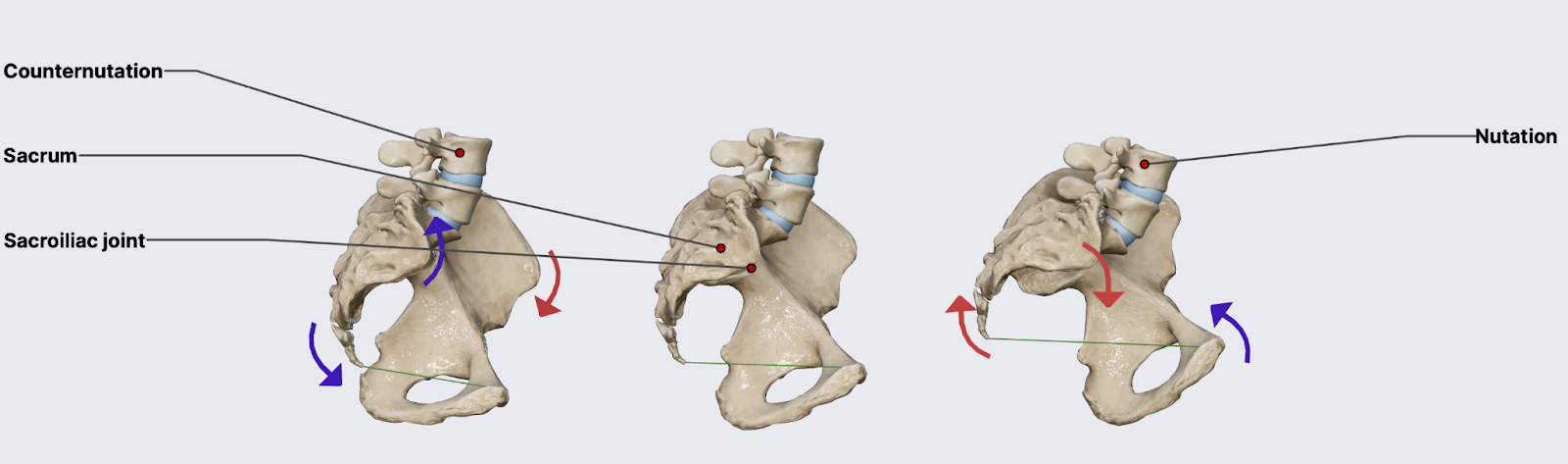
The sacrum can tilt in two instructions:
- Nutation: The highest of the sacrum ideas inward, towards the pelvic inlet. This widens the pelvic outlet from entrance to again because the tailbone shifts backward.
- Counternutation: The highest of the sacrum ideas backward, away from the pelvic inlet. This widens the pelvic inlet from entrance to again because the tailbone swings ahead.
These actions are most noticeable once we take a look at the general positioning of the pelvis:
- Anterior Pelvic Tilt (APT): The pelvis tilts ahead, and the sacrum strikes into nutation, opening the pelvic outlet.
-
Posterior Pelvic Tilt (PPT) : The pelvis tilts backward, and the sacrum strikes into counternutation, opening the pelvic inlet.
Why Pelvic Opening Issues for Labor and Beginning
As I discussed earlier than, the pelvic bones shifting could make area for child throughout labor and delivery. Infants don’t have a straight shot out. They take just a few turns as they maneuver the pelvis.
Early Labor – Coming into the Pelvis
The widest a part of a child who’s within the cephalic place is the child’s head from entrance to again. In most pregnant our bodies, the pelvic inlet is widest backward and forward. For this reason most infants enter the pelvis from the facet throughout early labor.
Lively Labor – Rotating on the Mid-Pelvis
As labor begins to show the nook into energetic labor, round 5-6cm, the child additionally turns 90 levels on the ischial spines on the mid-pelvis. That is the place the pelvic flooring begins and the child now has its head entrance to again within the pelvis.
Last Stage – Exiting the Pelvis
Labor forges ahead and the child strikes beneath the pubic bone and into the pelvic outlet. As soon as the top is out, the widest a part of the child is now the shoulders, so the child swings again round to have its again to the facet, so the broad shoulders can come by means of the pelvic outlet.
Creating Area for a Smoother Beginning
Inlet
Focus: Exterior rotation of the legs, counternutation of the pelvis and leg extension.
Listed below are some positions that encourage exterior rotation, counternutation, and leg extension to assist open the pelvic inlet.


- Rocking forwards and backwards or circling hip on a ball

- Baddha Konasana (Seated Butterfly Place)

- Standing legs turned out whereas winging the hips backward and forward

- In mattress with a peanut ball or huge pillow legs turned out

- “Flying cow lady” from Spinning Infants methodology

- Extensive knee however upright leaning on a ball or blocks

Mid pelvis
Focus: Asymmetrical positions of the legs (that means one leg is in a special place than the opposite). This helps create area inside the mid-pelvis, the place the child must rotate.
Discover these asymmetrical positions to encourage opening and mobility within the mid-pelvis:

- Strolling stairs
- Foot on a stool

- One leg on a yoga block on all 4’s


- Facet mendacity with a peanut ball or huge pillow

- Sitting with one leg on a peanut ball or pillow. This pose truly opens the mid pelvis and the inlet. It’s also nice for serving to child rotation!

- One leg in facet lunge/squat and one in virasana, sitting on two or three blocks.

- Asymmetrical facet mendacity with a peanut ball or huge pillow

Outlet
Focus: Inside rotation of the legs, Anterior Pelvic Tilt (APT) and Leg flexion past 90 levels (like a squat)
These positions encourage inner rotation, an anterior pelvic tilt, and deep squats to assist open the pelvic outlet.

- Facet mendacity with inner rotation and a peanut ball or huge pillow

- Facet mendacity inner rotation


- Knee’s in, toes out whereas standing and on again.


Whereas delivery is unpredictable, it’s empowering to have instruments that may assist you and your child and physique work collectively on this endeavor. Follow these totally different positions forward of time so they’re in your physique and you might be snug with them. Contemplate printing this out and tucking it in your hospital bag as a cheat sheet to remind you of positions you could need to attempt throughout labor.
FAQs
When ought to I begin doing these workouts?
You may start incorporating these workouts into your routine as early as your first trimester, however all the time hearken to your physique and cease when you expertise any ache or discomfort.
Can these poses assist with labor ache?
Whereas these workouts can not assure a pain-free labor, they may help put together your physique for a better path for child and the bodily calls for of childbirth, probably easing discomfort and selling a smoother labor.
What are the opposite advantages of those actions apart from getting ready for labor?
These positions may also assist to enhance posture, cut back again ache, stability the pelvic flooring muscle tissue, improve flexibility, and promote leisure and stress discount throughout being pregnant.

